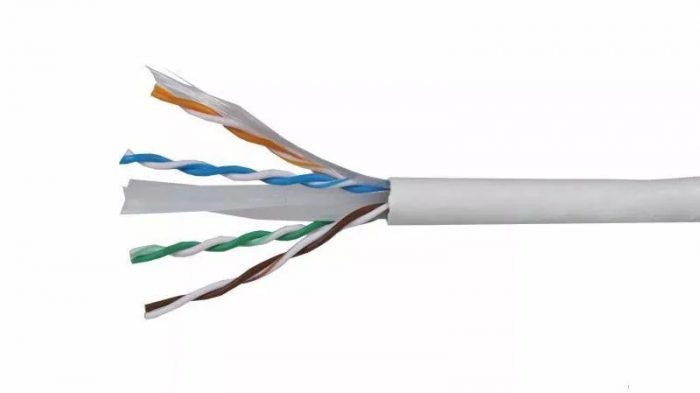
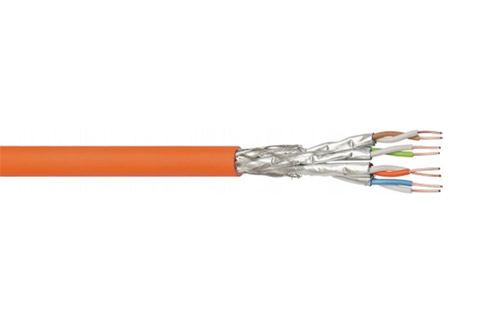
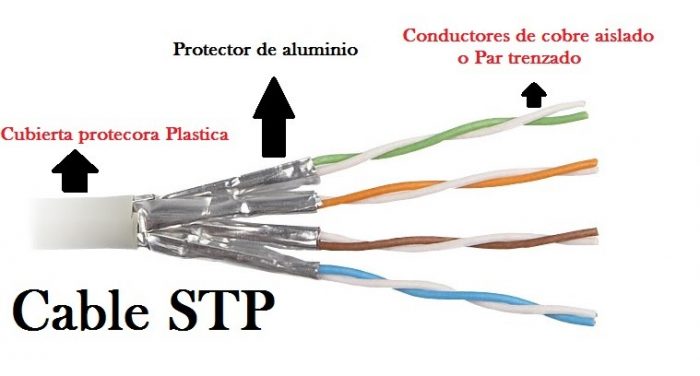
How to choose the network cable. Do you know everything about network cable? Network cables transmit electrical signals over long distances and are classified according to the maximum frequency that they support, based on technical standards and specific characteristics, such as the quality of the material used.
These standards must be followed by manufacturers, and manufacturing network cables is much more complicated than ordinary copper cables, since this type of material must be efficient at high frequencies, without signal attenuation or electromagnetic interference.
In this manufacturing process, attention must be paid to the appearance of impurities, bubbles and the entanglement of the pairs of cables, a critical factor for a satisfactory result. But, How to choose the right network cable for data traffic according to the IP protocol? Are the network cables available in the market compatible with the demand for innovative products launched today?
Check, in this article, everything related to the network cable: the types of cable available, their applications and characteristics that must be taken into account before buying products to avoid installing elements of dubious quality.
How to choose the network cable: Categories
There are several network cable standards on the market, which change according to frequency, that is, transfer speed of data that the material supports, and the ability to maintain the effectiveness of the transmission in case of complications. Despite this, little is said about the best application in each category and their respective shields, as we will see below.
Although Category 1, 2, and 4 cables are not recommended by the TIA (Telecommunications Industry Association) and are therefore no longer manufactured, Model 3 cables are still in use in telephone infrastructures: they were the first twisted pair cables developed and consist of at least 24 strands per meter (the number of strands changes to mitigate interference between pairs of cables).
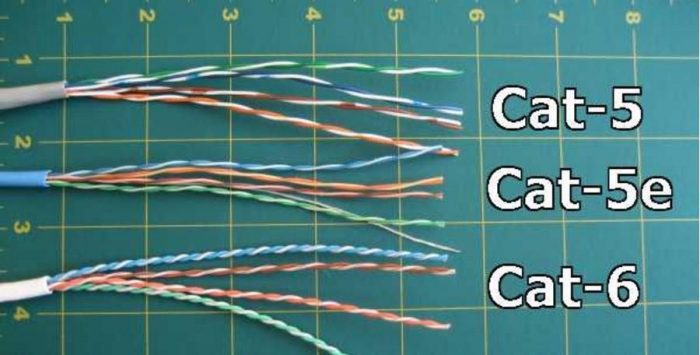
To find out the category of a cable, simply check the information plotted on its exterior. In this post we explain, in general, some of the most used classifications in projects: Cat5, Cat5e and Cat6.
Cat5 network cable
This is the oldest standard of network cables, widely used in home networks. Its data transfer speed ranges between 10Mbps and 100Mbps, but, currently, the use of this type of cable has been replaced by Cat5e standard, which supports the higher speeds demanded by the evolution of the equipment.
Cat5e network cable
This is the upgraded version of the Cat5 model. Cat5e cable is designed to support vspeeds up to 1000 Mbps, reduce infrastructure interference and minimize signal loss.
These improvements made it possible to use longer cables, almost close to the allowed current of 100 meters. Therefore, it is indicated for domestic and corporate installations.
Cat6 network cable
In this version, the interference level is low, and in some cases, the standard can support speeds up to 10 Gigabits and frequencies up to 250 MHz.
Home networks are unlikely to utilize the full potential of this cable model, so the best application occurs in locations where the total coverage distance of the cabling is greater than 10 meters to 55 meters.
The assembly scheme of the shielded FTP CAT5 network cable in the 568B standard is ideal for use in audio and video equipment that convert the signal into a CAT5 cable.
Category 6a was created to allow the use of network cables up to 100 meters in 10G networks, since they admit frequencies of up to 500 MHz and integrate measures that minimize the loss of signal and the appearance of interferences. between peers, called crosstalk.
One of these measures was to distance the pairs using a spacer, which increased the thickness of the cable by 2,3 mm (from 5,6 mm to 7,9 mm), reducing its flexibility.
What is the shielding of the network cable?
Another important aspect when choosing the network cable is the shielding made in the material. This is because it is necessary pre-assess the environment, in order to identify possible sources of interference in the transmission of signals. This makes them ideal for applications near transmission antennas and electrical networks.
Unshielded cables are generally more flexible and easier to crimp. For this reason, they are more affordable and popular on the market. There are also several models of shielded network cable, classified according to the type of shield, as described below.
UTP: Unshielded Cable
In the past there was no standard for braiding cables. This was because the demand for transmission was only for voice signals. This fact changed with the technical standardization of the manufacture of network cables.
Currently, it is necessary to service networks of up to 10.000 megabits and, to enhance transmission and inhibit interference, the balanced pair system is used: the same signal is sent in each pair, but with the polarity reversed.
FTP:Cable shielded twisted pair
Cables are those that use a simpler shielding: thin sheet steel or aluminum alloy, elements that involve all pairs of cables, protecting them from external interferences.
STP: Shielded twisted pair cable
In this model, the cables use a individual shielding for each pair of cables. This reduces crosstalk and improves cable tolerance for distance, which can be used in situations where non-standard cables need to be crimped, above 100 meters.
SFTP: Fully Shielded Twisted Pair Cable
Cables of this type combine individual shielding for each pair of cables with a second external shield, which wraps all the braids, making them especially resistant to external interference. Therefore, SFTP cables are best suited for environments with a high incidence of distortion.
The use of shielded cables should be combined with shielded RJ-45 connectors, which protect the unlocked part of the cable inside the connector.
How to choose the quality network cable
The choice should not be based on the superiority of the model. The most advanced standard cables, as well as being more expensive and difficult to find. You must choose the appropriate ones for the purpose for which they are intendedOtherwise, what happened with Cat6 cables in 10 gigabit networks will happen which, since their maximum distance was reduced to 55 meters, were replaced by the 6a standard.
Like any type of product, there are good quality network cables, that comply with the standards specified for the market, and cables with compromised performance, since their components have been changed by the manufacturer in order to reduce their costs.
Unfortunately, without specific meters, it is difficult to identify poor quality cables. In this case, it is recommended to use only trusted brands, produced by companies with a good history of sourcing and recognition in their product line.